thereMINI: Creating Music with Hand Gestures Using FREE-WILi for a Touch-Free Sound Experience
The Wearable Theremin! thereMINI is a wearable theremin using FREE-WILi to turn hand movements into music, translating motion into notes and volume for a touch-free, expressive sound experience.
🎶 thereMINI: A Wearable Theremin 🎶
Turning motion into music with FREE-WILi
🌟 Inspiration
We designed this as an accessibility device for one-handed music creation but soon saw its broader potential. Inspired by conducting, we mapped hand motion to notes and volume, making music creation more intuitive and inclusive. We continue to design this as a accessible device, but it is for everyone!
🎵 What It Does
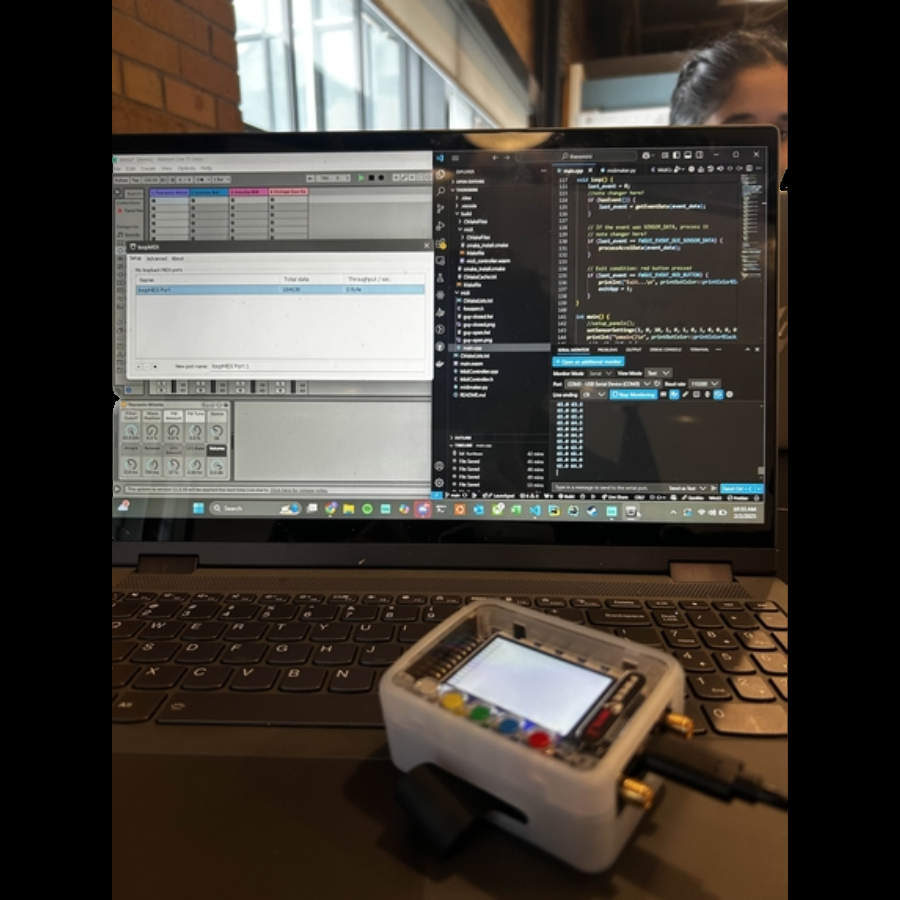
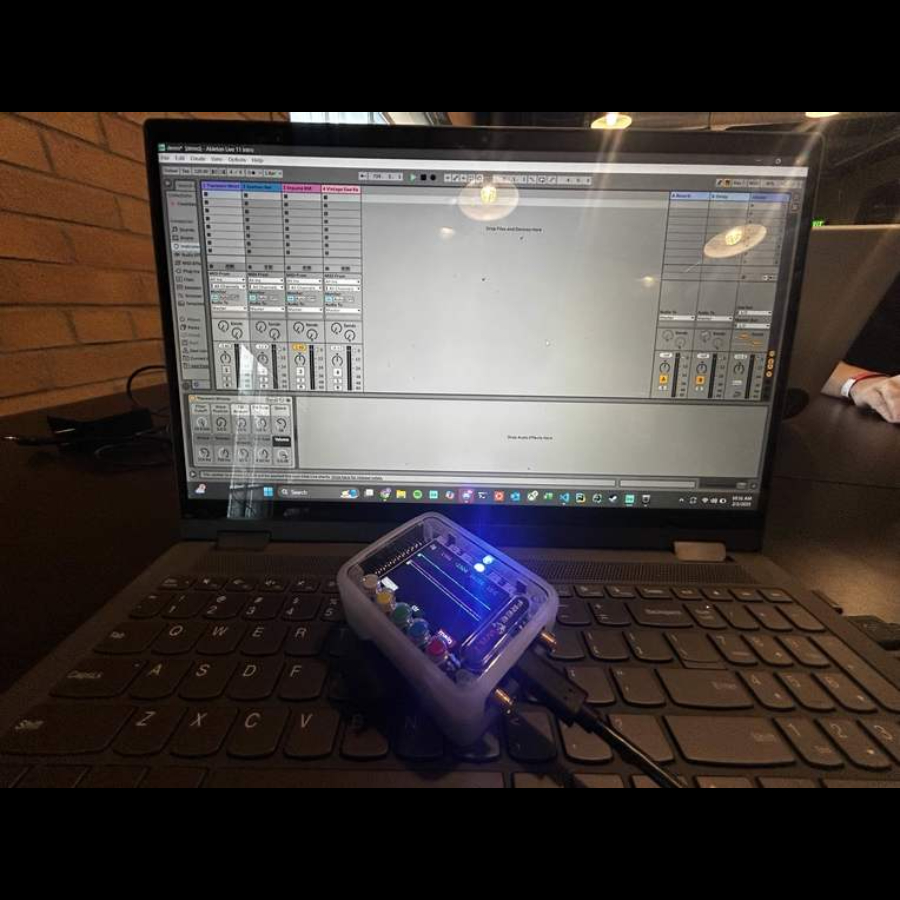
Using the FREE-WILi we were able to extract the accelerometer data as serial data. Converting said data to MIDI data (a music data type) we were able to use music software, like Ableton to translate it into virtual instrument playing. Moving your hand down increases volume and putting it down increases it. Moving your hand left or right changes notes, specifically a scale of 8 notes. Combining all that we can emulate a full virtual keyboard with just the movement of your hand!
🛠️ How We Built It
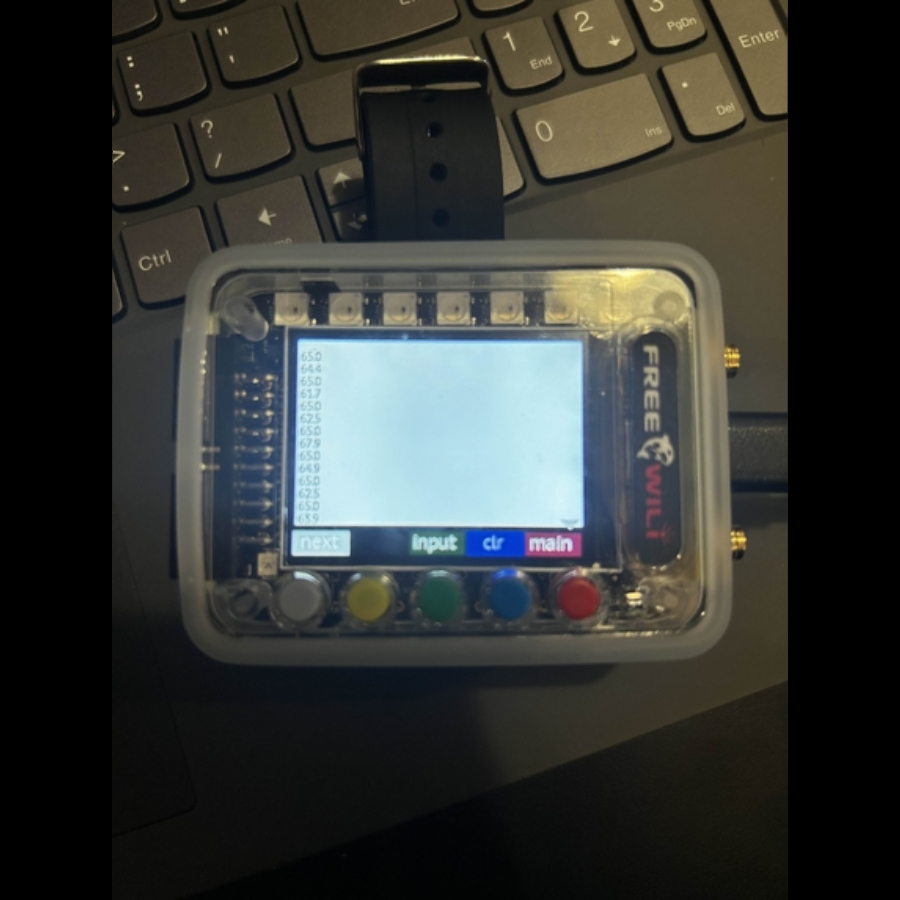
- Hardware: FREE-WILi device is a wearable microprocessor, outfitted with many sensors and capabilities, the one we focused on is the accelerometer. We used this mainly to translate xyz coordinates into angles, and then MIDI values for the notes and volume. This data is sent through USB serial data to be read by the software.
- Software: We used C++, and C to embed functionality for the FREE-WILi and python to clean and extract the data from it. loopMIDI is a software that creates a virtual MIDI controller that reads from our script, and feeds it to DAWs.
- Implementation: The horizontal rotation is used for the notes on a rotation of -90 -> 90 degrees, and the vertical rotation is used for lowering and increasing the pitch on -30 -> 30 degrees.
🚧 Challenges We Ran Into
We addressed USB port access challenges between WSL and Windows, ensuring proper connectivity. Translating accelerometer data into MIDI required refining sensitivity and applying filtering to improve accuracy. By optimizing data formatting and transmission, we facilitated seamless MIDI transfer. Through continuous troubleshooting and iterative testing, we achieved smooth integration between hardware and software.
🏆 Accomplishments We're Proud Of
Our project focused on turning complex tasks into key milestones. A major achievement was enabling MIDI data transfer from FREE-WILi to a computer, converting user movements into precise musical instructions like pitch and velocity. Our greatest achievement was the design of the notes and pitch to hand movements, and what was the most ergonomic and accessible way we would implement it.
📚 What We Learned
We learned how to process real-time sensor data into MIDI signals, ensuring seamless hardware-software integration. Designing for accessibility taught us the importance of intuitive and ergonomic control. Optimizing MIDI implementation required refining pitch, velocity, and minimizing latency. Through iterative problem-solving, we debugged formatting errors and fine-tuned movement sensitivity.
🚀 What's Next for thereMINI
We plan to enhance thereMINI with scale mode, chord mode, and octave control, mapped to buttons on the FREE-WILi for seamless switching. A GUI will provide visual feedback and customization options. Beyond development, thereMINI has potential as an accessible instrument, an innovative tool for musicians, and an educational device for learning music through motion.
Built With
ableton accelerometer c c++ freewili loopmidi pyserial python rtmidi