MeyesAI
Restoring more than vision.
MeyeAI: AI Intelligence for Assistive Navigation
We built an AI that gives any camera the spatial intelligence of a guide dog - turning smartphones, robots, or smart glasses into personalized navigation assistants for the visually impaired.
The Problem We Solved
1.3 billion people worldwide live with vision impairment. While guide dogs cost $50,000+ and take years to train, and white canes only detect ground-level obstacles, there's a massive gap in affordable, intelligent navigation assistance.
Our Solution: Beyond Hardware - A Spatial AI Platform
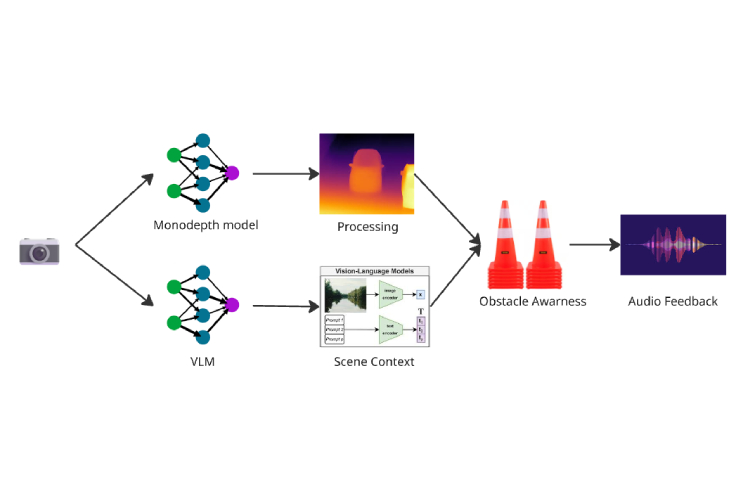
We developed an adaptable intelligence system that transforms any camera-equipped device into an assistive navigation companion. During the hackathon, we demonstrated this through:
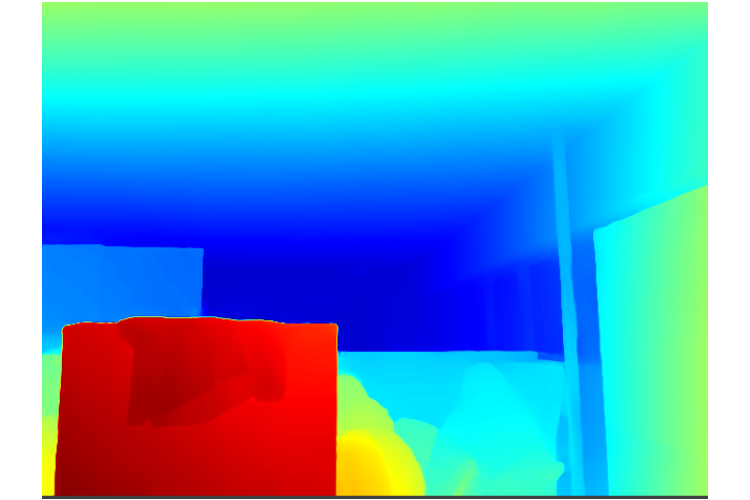
- Monocular Depth Estimation: Our AI extracts 3D spatial information from a single camera—no expensive LiDAR needed - making it deployable on everything from $50 smartphones to autonomous robots
- Real-time Semantic Understanding: We fine-tuned vision models to identify and track 100+ everyday objects, providing contextual awareness like "coffee table 3 feet ahead, doorway to your right"
- Vision-Language Model Integration: Our VLM can describe complex scenes beyond simple object detection—understanding activities ("someone is cooking"), reading text in the environment, and providing rich contextual descriptions of spaces
- Natural Language Navigation: Our LLM integration doesn't just detect objects—it understands intent. Users can ask "Where's the bathroom?" or "Find me a seat" and get intelligent guidance
- Responsive and Adaptive Feedback System: Spatial audio cues and conversational responses that adapt to each user's preferences
Technical Implementation
We built three proof-of-concepts in 24 hours:
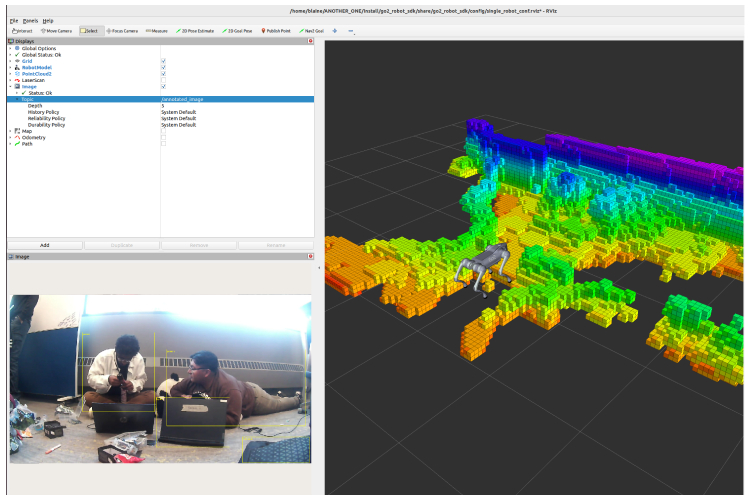
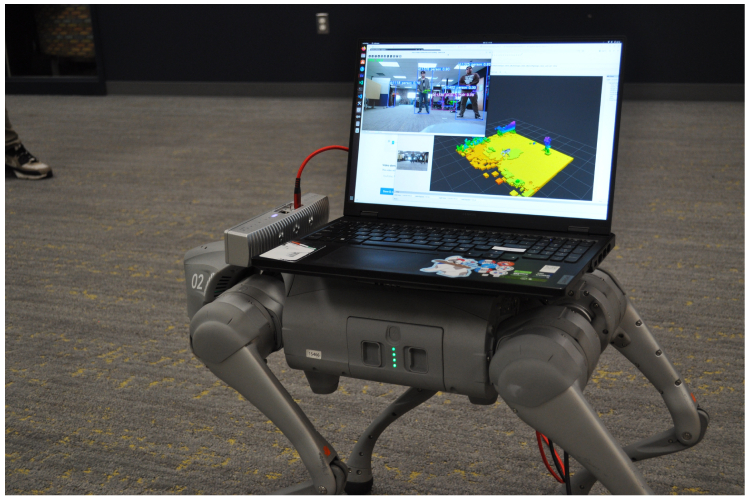
- Quadruped Robot Demo: Showcased autonomous navigation with real-time environmental understanding
- Web Application: Demonstrated smartphone compatibility, turning any phone into an assistive device
- API Framework: Proved our system can integrate with existing assistive tech, smart glasses, or IoT devices
Our Key Differentiators
- Magnitudes cheaper
- Instantly deployable
- Continuously learning
- Platform-agnostic
Impact Beyond Accessibility
While we're starting with visual impairment, Avis's spatial AI has applications in:
- Warehouse robotics for inventory navigation
- Elder care for fall prevention and medication reminders
- Search and rescue operations in low-visibility conditions
- Augmented reality gaming and education
How We Built It
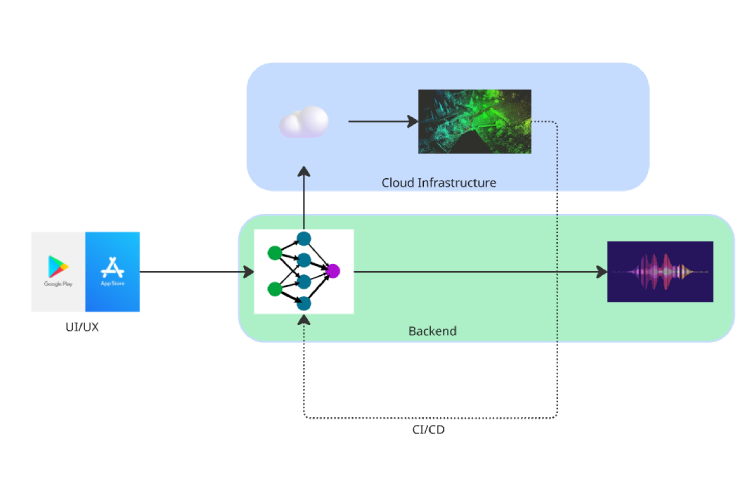
We architected Avis as a modular system with three core layers:
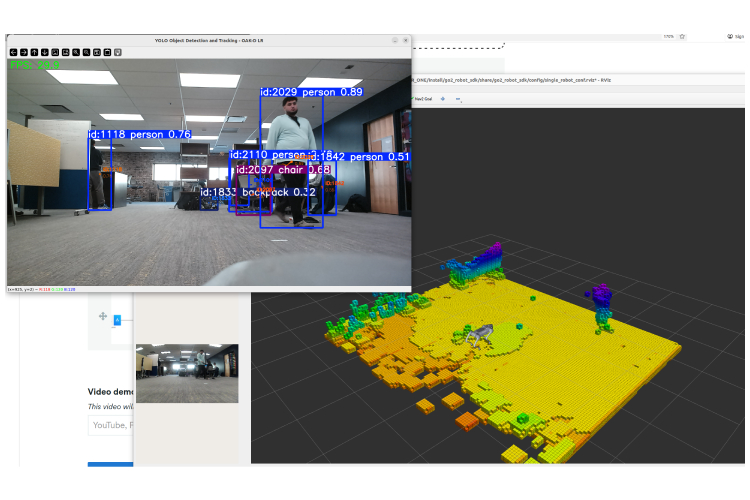
- Perception Layer: We developed multi-functional computer vision models combining monocular depth and VLMs. We also implemented state-of-the-art YOLO models for real-time object detection, optimizing them to run efficiently on edge devices
- Intelligence Layer: We connected LLMs for natural language understanding and created custom prompting strategies to translate visual data into helpful, context-aware guidance
- Interface Layer: We built ROS2 integration for the quadruped robot, a responsive React web app with WebRTC for real-time video streaming, and a RESTful API for third-party integrations
Our tech stack included Python for AI model deployment, JavaScript/React for the web interface, and ROS2 for robot control—all orchestrated through Docker containers for easy deployment.
Challenges We Faced
- Real-time Processing on Edge Devices: Balancing model accuracy with inference speed was crucial. We had to optimize our models to run at 15+ FPS on mobile processors while maintaining reliable object detection
- Sensor Alignment and Calibration: Getting accurate depth estimation from a moving robot required complex coordinate transformations and real-time calibration adjustments.
- Natural Language Generation: Creating descriptions that were informative but not overwhelming required careful prompt engineering and user testing to find the right balance.
- Local v. Cloud: The demanding requirements of real-time responsiveness required precise benchmarking of round-trip response times. ## What We Learned
- The Power of Monocular Depth: We discovered that modern AI can extract surprisingly accurate 3D information from single cameras, democratizing spatial computing
- Accessibility is About Choice: Through user feedback, we learned that different users want different levels of detail—some want just critical obstacles, others want rich scene descriptions
- Edge Computing is Essential: For real-time assistance, we had to move core processing to the device itself, teaching us valuable lessons about model optimization and quantization
- Interdisciplinary Design Matters: Building for accessibility required us to think beyond technical metrics and consider human factors like cognitive load, alert fatigue, and personal autonomy
Most importantly, we learned that the best assistive technology doesn't replace human judgment, it enhances it by providing the right information at the right time.
Next Steps
We're looking to continue the development of MeyesAI by partnering with local vision impairment organizations to refine our feedback systems with the goal of returning agency to visually impaired people around the world.
Built With
huggingface
javascript
llm
oakd
opencv
python
pytorch
react
ros2
unitree
vlm